Generators are used by companies and residences during power outages. Three-phase generators are the most prevalent because they function effectively and carry heavy loads. This makes them excellent for factories, huge businesses, and high-tech residences. Their three-phase power distribution stabilizes energy supply and reduces load changes that might damage sensitive equipment. Modern technology comes with the obligation to use it safely.
This article covers 3-phase generator safety. It includes generator location, fuel, and electrical safety. Correct installation is the first and most important step. A dry, airy, fire-free setting is essential. Secure the area to prevent youngsters and pets from entering. Installers should follow local electrical rules and get a plumber to connect electrical systems.
After installation, the generator needs ongoing safety and efficiency maintenance. Regularly check for gas or oil leaks, lines, and electrical wear or corrosion. Clean, well-maintained generator parts decrease accidents.
Installing correctly
Safely utilizing a 3 phase generator requires several steps. Installation requires a dry, well-ventilated, fire-free area. Store generators outside to avoid carbon monoxide buildup, which is dangerous inside. A stable, level platform will prevent the generator from falling and spilling fuel or producing an electrical problem.
After site safety, follow manufacturer installation instructions. The generator’s distance from walls and other buildings must be determined to minimize burning and provide enough cooling. Employ an electrician for long-term hard wiring. A professional will inspect your electrical lines for code compliance. Electrical concerns that might cause fires or short circuits are reduced.
Safely Handling Fuel
If mishandled, 3-phase generator gasoline may leak, spill, or explode. Use gasoline, diesel, or propane recommended in the generator’s manual and keep it in fuel-approved containers. Ensure ventilation and keep these goods away from heat and fire. Running or heating the generator shouldn’t fill it. Let it cool to avoid flames.
Avoid fuel leaks before and during operation. If leaks are found, turn off and service the generator before beginning. Fuel storage incidents may be avoided by marking zones and training staff on gasoline handling. Establish spill response procedures to react swiftly to unnoticed spills.
Knowing electrical safety rules
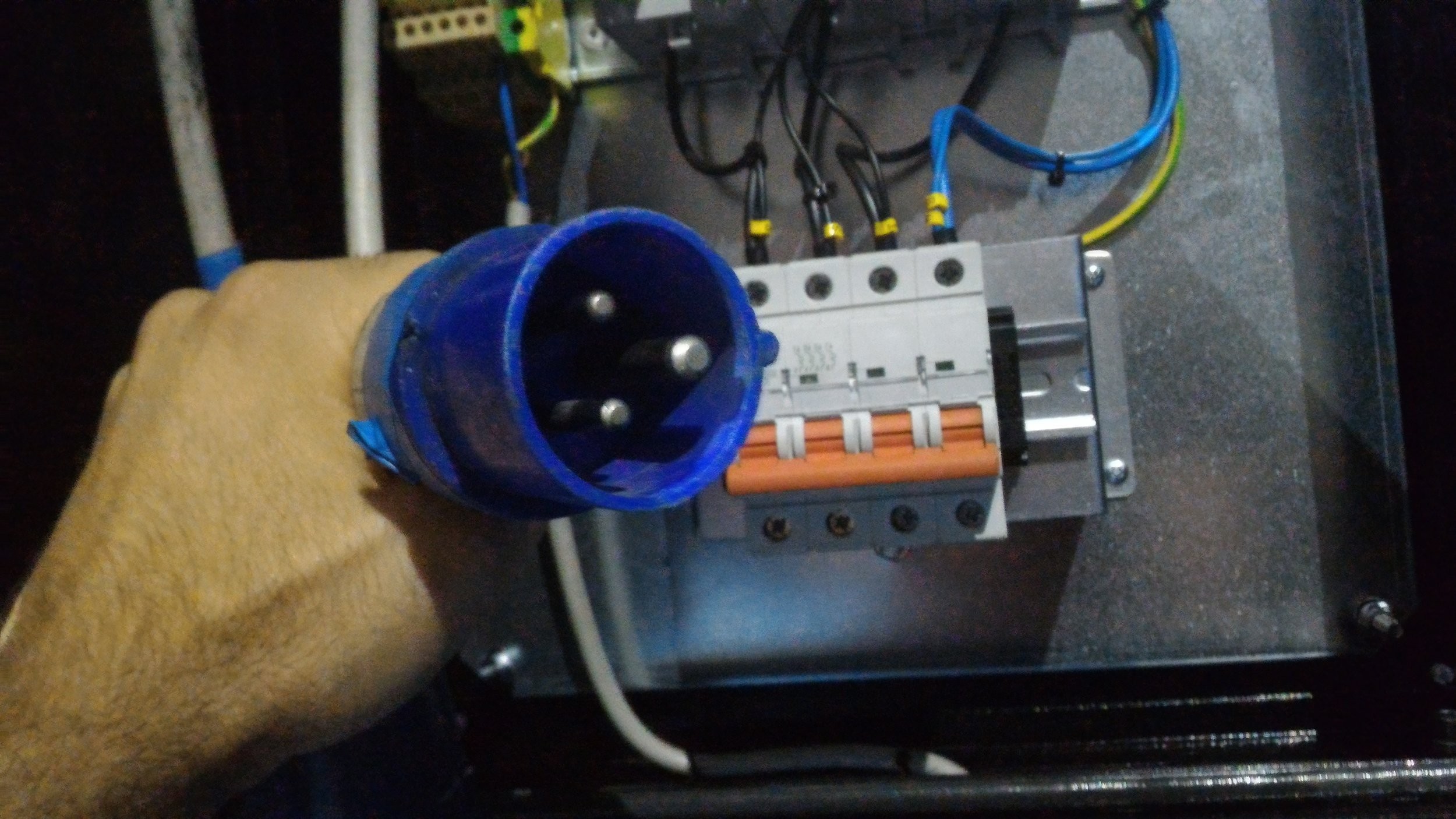
Using a 3-phase generator requires electrical safety. Unmanaged generators produce dangerous high-voltage power. Before utilizing the generator, ground it per manufacturer’s instructions. Grounding safely transfers surplus energy into the soil as shock and fire prevention.
Use high-quality, rated outside extension cords to connect devices to the generator. Check cables for damage or wear to prevent short circuits and fires. Use generator’s rated power. Checking load avoids harmful generator burns.
Inspecting and maintaining
The 3-phase generator needs frequent maintenance for safety and efficiency. Maintaining a generator reduces breakdowns and ensures consistent power. Oil, cooling, air filters, and fuel systems should be checked regularly to detect problems early. Always plan maintenance per the manufacturer’s service handbook.
Check eyes before use. Check for wear, corrosion, and damage. Corroded or poorly built electrical wires are dangerous. To ensure generator dependability and readiness, load test it yearly. A repair log including timing and information may be useful. This aids organization and accountability.
Emergency awareness and readiness
Safety precautions may not prevent accidents with a 3-phase generator’s many duties. These unavoidable events need a generator-compatible disaster plan. This technique guarantees everyone to respond quickly and effectively to unexpected events, eliminating risks and damage.
Training all workers is essential for emergency response. This training should include power, motor, and fire situations. Operators must identify and resolve issues. They should know engine shutdown safety. A fast shutdown may avoid fuel spills or electrical risks.
Conclusion
Safety is key while using three-phase generators. Proper generator installation, fuel management, electrical standards, and maintenance limit generator risks. A strong disaster preparation program offers people confidence that all required steps have been done to address difficulties, making things safer. These factors guarantee 3-phase generators function safely and protect workers and the environment.